Ever Wondered Why Computers Need Operating Systems? Here’s the Answer

Introduction
Have you ever wondered how prime ministers and presidents of different countries communicate with each other? Learning the complete language of every country would take a lot of time, and these leaders have to deal with many nations. So, how do they solve this problem?
The answer is simple: they always keep interpreters with them. An interpreter is an expert who knows two or more languages, both spoken and written. The interpreter translates the language spoken by one person into the language of the other person. In this way, both people are able to understand each other and communicate effectively.
The same concept applies to operating system in a computers.
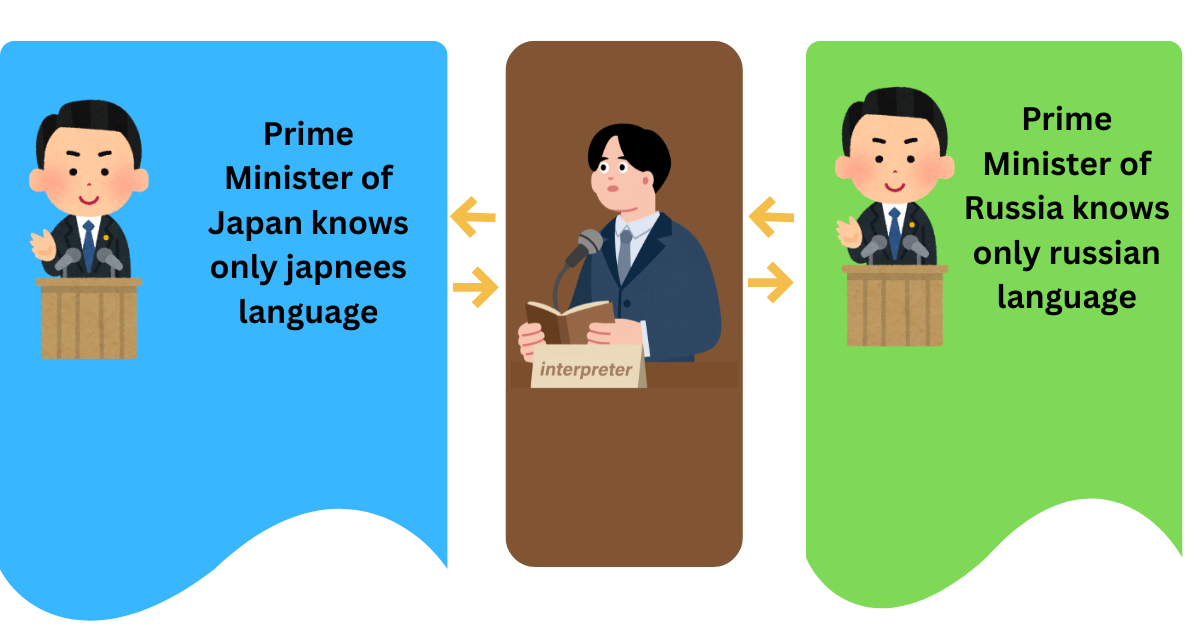
Before explaining further the exact concept of an operating system, I would like to share my own experience of how I first understood this idea when I started learning about computers.
Back in 2001, when I enrolled myself in a two-year Advanced Computer Diploma course at an Aptech center, I was introduced to the fundamental of computer and operating system. During that time Windows XP and Windows 2000 operating system were quite popular and widely used.
In those early learning days, one of my instructors explained the role of an operating system in a very simple and memorable way. The explanation was also mentioned in the Aptech book “Know Your Desktop.” According to it, an operating system acts as a mediator between the user and the computer hardware.
User cannot directly communicate with the computer hardware. Instead, the user interacts with the operating system, which understand the user commands, interprets them, and then converts those instructions into machine language so that the hardware perform the required task.
This simple explanation helped me clearly understand why an operating system is essential for any computer system.
In this blog, we will clearly understand:
What an operating system is
Why it is important
- Journey of the operating systems
Its main functions
Types of operating systems
Real-world examples
What is an operating system and why does it required?
An Operating System (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs.
In simple words, the operating system:
Starts your device
Allows you to use apps and software
Manages memory, processor, files, and devices
It is needed because:
- It provides an interface to the user to interact with other connected hardware devices link printer, scanner and more.
- Operating system carries all the required application and utility softwares for users to perform certain tasks.
- It is also required to setup computer network where one computer communicate with other computers in Local Area Network or LAN.
- To install and uninstall sofwares.
- To view the status of connected hardware devices.
- To view the status of Internet and network.


Computers and Programming Languages
We, as computer users, do not understand the language of computers directly. Computers and machines do not understand human languages. They only understand binary language, which consists of 0s and 1s. These binary values represent electrical signals known as ON and OFF states.
Here Operating system plays the vital role and act as an interpreter between the user and computer system.
Software programmers use programming languages such as C, C++, Java, Python, and many others to write instructions. These programming languages are later translated or interpreted into machine code so that the computer can understand and execute them.
Software and Programs
To understand software, we first need to understand what a program is?
A computer program is a set of instructions written using a programming language like C, C++, Java, and others.
A software is a group of such interconnected programs. To use a software, it must be installed on the computer by running its setup file. When all the required programs are successfully loaded, the user can interact with the computer and use the software effectively.
In Short
Program → A set of instructions
Software → A group of programs
Types of software in a computer
- System software
- Application software.
System software
This software works to provide service to computer hardware, data, program files and other application software.
It is a type of interpreter that tells the user by translating the language of the machine.
The computer knows only one language, which is the language of 0 and 1, 1 means true or on and 0 means false or off.
But computer is an electrical and electronic machine then how does computer know what are 0’s and what are 1’s?
Computers only send and receive electrical signals and have a standard code for each character.
Let’s understand it like this – as soon as you type A from your computer’s keyboard, a standard code goes in the computer which is ‘1000001’ All these types of codes which are also called ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) . All these codes are executed by loading into RAM (RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY) from the hard drive of the computer.
So when you press the button A (1000001) from the computer, your keyboard sends current through 7 wires to the computer.
The first wire represents 1, then the current goes through the first wire, the computer does not get current through the remaining 2,3,4,5,6 wires which display 0. After this the current goes through the 7th wire. Boom! Now the computer comes to know that you have sent the code for A to the computer and it is displayed on your computer screen with the help of the circuits in the computer.
System software works to coordinate between computer hardware resources and the user. Therefore, the system software itself is called the operating system.
Application Software
This software is created to perform a certain task which is written by a programming language like C, C++, JAVA etc. and installed in the computer system. For example Electricity Bill Management System, Dealership Management System etc.


Why it is important?
- Operating system makes computer user friendly and provides all services which is required by the user.
- Operating system runs multiple programs at the same time.
- It protects data of the system through its data security feature from viruses and threats. However it is always recommended to get highly secure and dedicated antivirus software installed on the computer with minimum 1 year of subscription. Some of them are Quick Heal, Norton, MacAfee, Kaspersky and more.
- It also controls hardware efficiently.
The journey of the operating systems 🌴🌴
It started with a computer that used to do one thing at a time, like a calculator🧮 . The BASIC operating system was introduced in the 1950s, which ran different programs automatically. In those days the computer operating system was not built for complex operations.
In 1960, hardware features like parallel processing, runtime libraries, interrupts were included.
Personal computers came in the 1980s and the operating systems present in them were exactly the same as used in large computers before this.
MAC OS is a graphical operating system created and sold by the Apple company. Its first OS was released in 1999 which is Mac OS X Server 1.0.
Main functions of an operating system
Process Management
The OS decides:
Which program runs first
How long it runs
When it stops
This allows multitasking, such as listening to music while browsing the internet.
First, the operating system has to make sure that each process and application gets enough processor time to function properly, and then use as many processor cycles as possible.
One of the main functions of the operating system is the scheduling of the work to be done by the processor. CPU has to process a lot of instruction simultaneously so scheduling is required which is managed by operating system. The operating system has to switch between different processes at the rate of thousands of times per second.
Processes are controlled and scheduled by the operating system for execution by the CPU. The operating system allows the application to start and suspend execution only if the interrupt is long enough and is interrupted by the user.
Memory Management
The operating system manages:
RAM usage
Allocation of memory to programs
Freeing memory when programs close
RAM (Random Access Memory) is also known as temporary memory where it stores data for currently running applications. CPU fetches data from RAM for processing. Its temporary because data inside the RAM gets disappeared once power is off.
An Operating system allocates space to ongoing programs, tracks the usage of RAM.
This prevents system crashes and slow performance.
File System Management
The OS organizes data in the form of:
Files

Folders

Directories
It helps users easily store, retrieve, and delete data.
Device Management
Operating systems control devices like:
Keyboard
- When you hit the button of keyboard it closes the electric signal
- Through keyboard controller it sends signal (scan code) to the processor which alerts the operating system
- Operating System then converts scan code into one charater ( like !, B , %, @, 2 etc) or converted into command then send an event to active applications for display or action. Learn More
Mouse
- Mouse is pointing device in a computer.
- It has two buttons on top of it which is “Left and Right” button and tiny wheel in the middle for scrolling the screen up and down or to zoom in or zoom out of screen by pressing control key or Ctrl key.
- It controls the motion of a pointer in two dimensions in Graphical User Interface on computer.
- Pointer can move in any direction of the screen and makes computer work simpler. Learn More
Printer
- It is used for printing the contents of computer on paper which can be text, images, letters, graphs etc. Learn More
USB devices
- It is an external storage device that can be connected to the computer’s USB port for data transferring. Learn More
The OS uses device drivers to communicate with hardware.
Security & Access Control
The OS:
Protects data from unauthorized access
Manages user accounts and passwords
Prevents malware and threats
Security is a major responsibility of modern operating system
Types of Operating System
Batched Operating System
Batched Operating System for tasks like Payroll System, Transactions Process. Batch operating system execute jobs in batch automatically.
Multi-Programmed Operating System
A multiprogrammed operating system is an operating system that keeps multiple programs (jobs) in main memory at the same time and switches the CPU between them to make better use of the processor.
How It Works
Several programs are loaded into memory.
Only one program runs on the CPU at a time.
If the running program needs I/O and must wait, the OS quickly switches the CPU to another program.
This continues, keeping the CPU busy most of the time.
Key Features
Multiple programs in memory at once
Better CPU utilization
Reduces idle time of the processor
Improves system efficiency
Example
Imagine a teacher checking notebooks:
While one student is writing (waiting), the teacher checks another student’s work.
Similarly, the CPU works on another program when one program is waiting.
Timesharing Operating System
A Time-Sharing Operating System is an operating system that allows many users or programs to use the computer at the same time by sharing CPU time.
Simple Explanation
In a time-sharing OS, the CPU gives a small time slice (quantum) to each program or user one by one. This switching happens so fast that everyone feels the system is working simultaneously.
How It Works
Multiple users/programs are present in the system.
The CPU runs one program for a very short time.
After the time slice ends, the CPU switches to the next program.
This cycle repeats continuously.
Key Features
Fast response time
Supports multiple users
CPU time is divided into small slices
Uses preemptive scheduling
Example
Think of a teacher answering questions:
Each student gets a few seconds to ask a question.
Then the teacher moves to the next student.
Everyone feels attended to.
Distributed Operating System
In a distributed OS, many computers are connected through a network. The user does not feel the difference between them and uses the system as if it were one computer.
How It Works
Multiple computers (nodes) are connected by a network.
Each computer has its own CPU and memory.
The distributed OS coordinates tasks among all computers.
Work is shared to improve performance and reliability.
Key Features
Resource sharing (CPU, memory, files)
Transparency (user sees one system)
Scalability (easy to add more computers)
Fault tolerance (system keeps running if one node fails)
Example
Imagine a group of workers:
If one worker is busy, another takes the job.
The work continues smoothly.
Real-Time Operating System
A Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) is an operating system that is designed to respond to inputs and events within a fixed, guaranteed time limit.
Simple Explanation
In an RTOS, correct timing is as important as correct output. If a task is completed late, the system is considered to have failed—even if the result is correct.
How It Works
Tasks are assigned priorities.
The highest-priority task gets the CPU first.
The system ensures tasks meet their deadlines.
Interrupts are handled immediately.
Types of RTOS
Hard Real-Time OS
Missing a deadline is unacceptable.
Example: Airbags, pacemakers.
Soft Real-Time OS
Missing a deadline is undesirable but tolerable.
Example: Video streaming, online gaming.
Key Features
Deterministic response time
Priority-based scheduling
Minimal latency
High reliability
Example
Airbag system in a car:
Sensors detect a crash.
Airbag must deploy within milliseconds.
Any delay can be dangerous.
Memory Management
In memory management, the operating system has to perform two major tasks. First of all, it is ensured that each process gets enough memory for execution and does not run into the memory space of other processes.
There are different types of memory in a system, using them properly so that the process can run properly. The task of the operating system is to set memory limits for any software and individual applications.
For example, if we imagine a machine that has 1 megabyte of RAM. Now when the computer starts, first of all, during the process of computer booting, the operating system requires some space in the RAM to load itself, So let’s assume that the operating system needs 250 KB to run. Now after the operating system is loaded in RAM, various types of driver software starts loading to control the computer hardware.
So in a hypothetical computer, let’s say the drivers require 250 KB. So 250 KB for operating system and 250 KB for driver software, then complete 500 KB is saved in RAM. Now the applications start loading into the memory through the operating system and they are in a block size whose size is determined by the operating system. If the block size is 2 KB, then each process that is loading gets a piece of memory that is 2 KB, and all applications follow this fixed block size. These block sizes ensure that no block should get space of each other.
RAM has limited space, so it can be increased by adding another RAM, but it doesn’t make any sense if the processor accesses only one memory location at a time, so RAM remains unusable even after having more than one RAM. So hard disk space is cheaper than RAM and if the information located in RAM can be sent to the hard disk, then the space of RAM will increase many times, that too without any cost. This technique is called virtual memory.
Memory types are given here :
- Cache memory – This memory is a very fast memory which is closest to the CPU. Controllers of this cache memory with less memory find out what data the CPU needs to process and send that data to the cpu by taking it out of the RAM very fast. This is a kind of buffer memory, data is always located for the process of CPU.
- Main memory – Random Access Memory in which all programs are loaded to work. It is of volatile nature and data cannot be stored in it.
- Seondary Memory – This is called a permanent storage memory and all the program files are stored in the c:/ drive . It is advised not to store valuable data, personal files, photos, videos etc. in this drive to avoid any loss of the data in the time when operating system corrupts and one has to format the c:/ drive and reinstall the fresh operating system. It is better to take backup of your valuable data every time. This memory is more in size and stores data and applications permanently. This memory works like virtual RAM and is controlled by the operating system.
Device Management
Any hardware device installed in the computer cannot be made functional until there is a method to operate that device. A program is required to operate these devices and these programs are named as device drivers. Device means equipment and driver means the computer program that will run this device.
For example, let’s assume that a computer hardware device is a car and it cannot run on its own until a driver comes and starts the car and drives it. Similarly, the same function is performed by the device driver in the computer.
We can say that operating system is the soul of computer without which computer is nothing but just a metal box. It contains many software applications inside itself, in which the software applications are able to work.
Over to You! ❤️
“I really appreciate you taking the time to read this blog. Your thoughts and feedback mean a lot to me, so I’d love to know your opinion in the comments!”![]() Drop your thoughts in the comments.
Drop your thoughts in the comments.![]() Share this post with your tech-loving friends.
Share this post with your tech-loving friends.![]() Follow us for more future tech insights.
Follow us for more future tech insights.

Hi
[…] VIJAY WASNIK 08/12/2022 […]
[…] Torvalds gave us Linux Operating System and Git. It gives power like an electricity to major IT infrastructure in the […]
[…] is the most widely used operating system across the world, powering millions of desktops, laptops, tablets, and even servers. Its […]
Logging into joygamelogin was pretty straightforward. Nice and simple. No problems there! See for yourself: joygamelogin
Aajogobr1, aka Spacy Cassino, isn't bad at all! I definitely get a few laughs playing on here. This review's got me playing for another hour now! Here's a link: spacy cassino.