Blockchain Technology: A Revolutionary System

When I first heard the word Blockchain Technology, I couldn’t help but wonder — why would anyone block the chain? In Hindi, the word “chain” means peace. We often say “chain se sone do” which means “let me sleep peacefully.” So naturally, I thought it had something to do with blocking peace! 😅
This is the beauty of language and curiosity — without proper knowledge, our minds can imagine anything. But once I learned about it, I realized blockchain has nothing to do with sleep or peace (though it might give you peace of mind in digital transactions!).
Technology has always been about solving problems — from the invention of the wheel to the smartphone in your hand. But in the last decade, one word has been making waves across industries, governments, and even everyday conversations: Blockchain (often called Block Technology).
So, let’s dive in and truly understand what Blockchain Technology is all about.
Introduction
You’ve probably heard the word Blockchain Technology mentioned alongside Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. And while it’s true that blockchain is the backbone of digital money, it’s much more than just a way to trade coins online. At its core, blockchain is a revolutionary system for storing, securing, and sharing information in a way that is nearly impossible to tamper with.
Think of it like digital Lego blocks. Each block represents a piece of verified information — transparent, secure, and locked in place. Once these blocks are added, they’re linked together in a chain, forming a permanent record of truth. No one can sneak in and change a block, and because the system is decentralized, no single authority controls it.
This unique design means blockchain doesn’t just power cryptocurrencies; it’s also transforming how we exchange money, verify identities, track goods, sign contracts, and even vote in elections. In a world where trust is often scarce and digital fraud is on the rise, blockchain offers a much-needed solution: a technology that builds trust without requiring us to blindly trust anyone at all.
In this blog, we’ll break down blockchain technology, how it works, why it’s important, where it’s used, and what the future looks like in 2025 and beyond.

What Is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology ensures that once data is stored inside a block, it cannot be deleted or modified without the consent of the entire network.
In simple terms, blockchain is a distributed digital ledger — a special type of database that records transactions or information in “blocks,” which are securely linked together in a continuous chain.
Each block contains valuable data (such as financial transactions, contracts, or records).
Once a block is filled, it is locked and permanently linked to the previous block, forming an unbreakable chain.
The entire system is decentralized, meaning no single company, government, or authority owns or controls it.
To imagine it better, think of a notebook that isn’t stored in one office, but is instead copied and updated across thousands of computers worldwide. Once a note is written in that notebook, nobody can erase it. Everyone can see it, verify it, and trust that it hasn’t been secretly changed.
That’s the power of blockchain — a technology built on trust, transparency, and security.
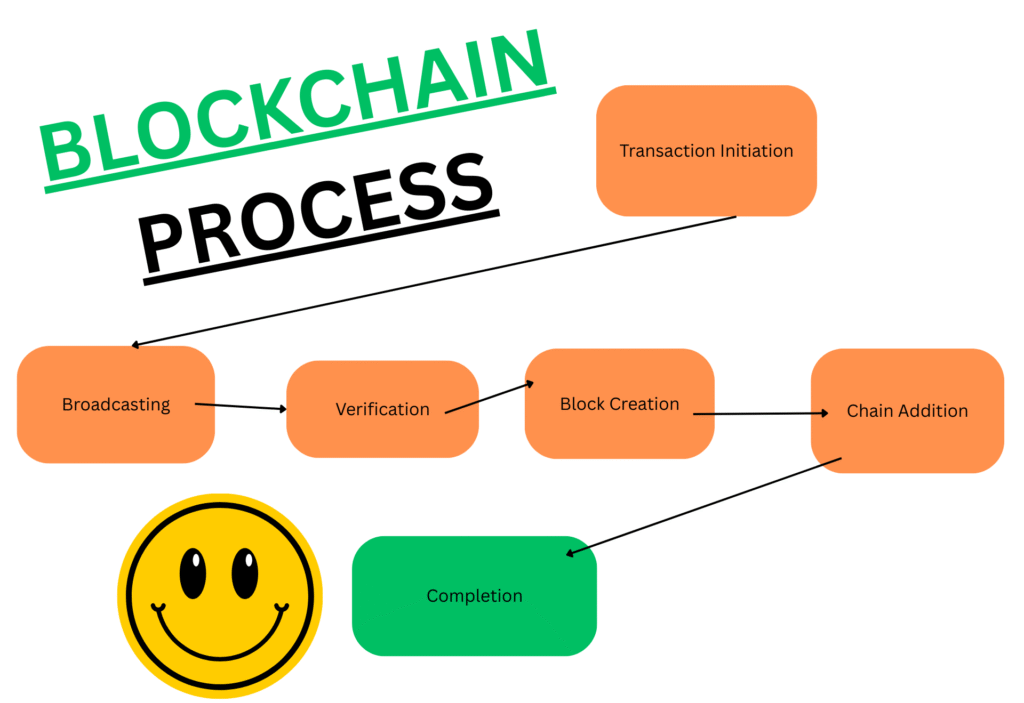
How Does Blockchain Work?
Let’s understand this with help of an example:
Transaction Initiation: Sita wants to send money to Ram.
Broadcasting: This transaction is shared with a network of computers (nodes).
Verification: The network validates the transaction using complex algorithms.
Block Creation: Once verified, the transaction is bundled into a block.
Chain Addition: That block is added to the existing blockchain, permanently recorded.
Completion: Ram receives the money, and the transaction is visible to everyone on the blockchain.
This process ensures security, transparency, and immutability — the three pillars of blockchain.
Features of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralization –
Centralization means that a single entity — usually someone at the top level, such as a company, government, or organization — takes full control of the network, data, and transactions. In this setup, all the decision-making power is concentrated in one authority, and all the data is stored and managed on a centrally located server.
The problem? If that central authority gets compromised, hacked, or corrupted, the entire system collapses. It becomes a nightmare for the whole network because everything depends on that one point of control.
Decentralization, on the other hand, distributes the decision-making powers across multiple nodes (computers) in the network. Instead of relying on a single authority, every node actively participates in verifying and approving transactions. This means no single point of failure, making the system more secure, transparent, and trustworthy.
In simple words:
Centralization = One boss controlling everything.
Decentralization = Power shared by everyone in the network.
- Transparency – Transactions are visible to all participants In traditional systems, only banks or central authorities can see and verify financial transactions. With blockchain, things are different. Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger that is accessible to all participants in the network. This doesn’t mean your personal details are exposed, but the transaction itself (like a transfer of value) is visible and traceable. This transparency helps build trust among users, as everyone knows that the data is authentic and verified.
- Immutability – Once data is added, it cannot be changed
One of the strongest features of blockchain is its permanence. When a transaction is added to a block and that block is locked into the chain, it becomes unchangeable. No one can go back and delete or alter the information — not even the system administrators. This prevents fraud, ensures historical accuracy, and makes blockchain a reliable source of truth. Imagine writing in a notebook where, once the ink dries, it can never be erased. That’s how blockchain works. - Security – Encryption makes tampering nearly impossible
Blockchain uses advanced cryptography (complex mathematical codes) to secure data. Each block contains a unique digital signature, known as a hash, which makes it virtually impossible to tamper with. If anyone even tries to alter a single block, the hash changes instantly, breaking the chain and exposing the fraud. This strong security system ensures that hackers can’t manipulate the data without being noticed. Consensus Mechanisms – Transactions are approved by majority agreement
Unlike centralized systems where one authority decides whether a transaction is valid, blockchain uses consensus mechanisms. This means that a majority of nodes (participants) in the network must agree before a transaction is approved and added to the chain. Popular methods include:Proof of Work (PoW): Used by Bitcoin, where computers solve complex puzzles to validate transactions.
Proof of Stake (PoS): Used by newer blockchains like Ethereum 2.0, where validators are chosen based on the number of coins they “stake” as collateral.
These mechanisms ensure that no single entity can control the network, keeping the system fair, democratic, and tamper-resistant.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
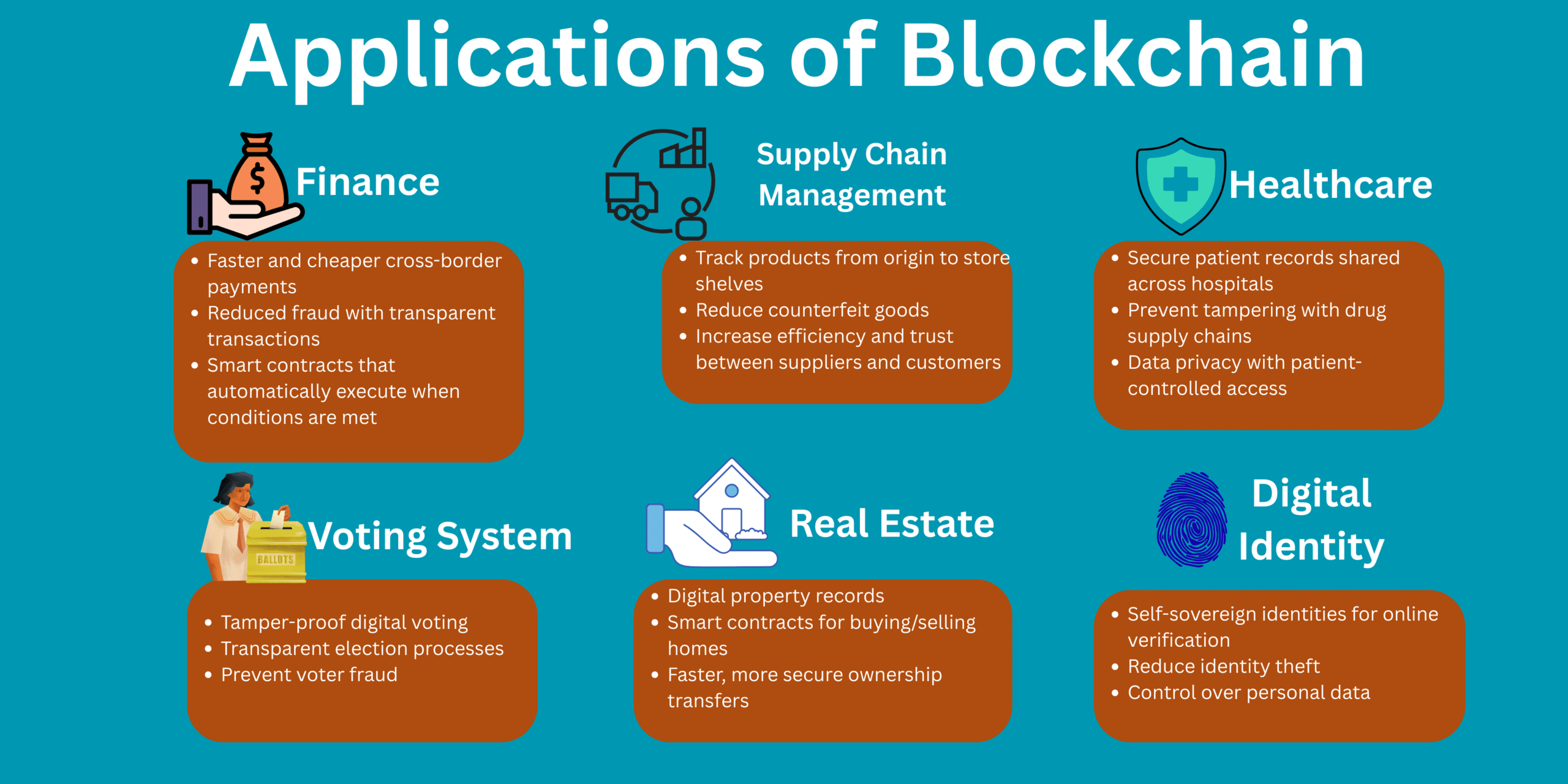
Benefits of Blockchain Technology 👍
Trust – Removes the need for middlemen
In traditional systems, we usually depend on banks, brokers, or authorities to establish trust between two parties. Blockchain eliminates this dependency by providing a trustworthy system on its own. Every transaction is verified, recorded, and stored permanently on the blockchain, meaning you don’t have to “trust” a middleman — you trust the system itself. This opens up direct peer-to-peer interactions, whether it’s money transfers, contracts, or data sharing.Speed – Faster processing of transactions across borders
Sending money or completing a transaction through banks can take days, especially across borders due to multiple checks, intermediaries, and different time zones. Blockchain speeds this up drastically. With no middlemen and real-time validation, transactions can happen within minutes, or even seconds, no matter where in the world you are.Cost Efficiency – Reduced fees compared to traditional systems
When you use banks, online payment platforms, or international remittance services, you’re often charged hefty fees for transfers, conversions, and service charges. Blockchain cuts out the middle layers, which means lower costs for users. For businesses, this can save millions of dollars in transaction fees, making blockchain a cost-effective alternative.Security – Advanced encryption makes hacking extremely difficult
Blockchain uses state-of-the-art cryptography to secure every transaction. Each block is linked to the previous one through unique digital fingerprints (hashes). If someone tries to tamper with even one block, the entire chain exposes the alteration immediately. This makes hacking incredibly difficult, if not practically impossible, especially in large networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum.Transparency – Everyone on the network can verify transactions
Unlike traditional systems where only authorized entities (like banks or government agencies) can view and approve transactions, blockchain offers open visibility. All participants in the network can verify, audit, and track transactions themselves. This level of transparency prevents corruption, fraud, or hidden manipulation. For example, in supply chain management, blockchain lets companies and consumers track the journey of a product from the factory to their doorstep.
Challenges of Blockchain Technology 🙄
Scalability – Handling millions of transactions is still difficult
While blockchain is powerful, most public blockchains struggle when it comes to scaling up. For example, Visa can handle around 65,000 transactions per second, but Bitcoin processes only about 7 per second, and Ethereum roughly 15–30 per second. This gap makes it difficult for blockchain to compete with traditional systems in terms of volume. Developers are working on solutions like sharding and Layer-2 technologies (e.g., Lightning Network, Polygon), but true scalability is still a big hurdle.Energy Consumption – Mining requires massive electricity
One of the most criticized aspects of blockchain, especially Bitcoin, is its energy-hungry mining process. Proof-of-Work (PoW) systems require miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles, consuming vast amounts of electricity. Reports have shown that Bitcoin mining consumes more energy annually than some small countries. While newer models like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are much more energy-efficient, the environmental impact of older blockchains remains a pressing concern.Regulatory Uncertainty – Governments are still figuring it out
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies exist in a gray area legally. Different countries have different approaches — some embrace it, some restrict it, and others ban it altogether. This lack of global regulation creates uncertainty for businesses and investors, who are unsure how laws may change in the future. For example, tax rules for crypto profits vary widely, and governments are still debating how to prevent misuse (like money laundering) without stifling innovation.Public Awareness – Limited understanding among common people
For many, “blockchain” still equals “Bitcoin” — and that’s where the knowledge ends. The broader applications of blockchain, like in healthcare, supply chains, or real estate, are not widely understood. This lack of awareness and education slows down adoption, because businesses and everyday people are hesitant to trust or use something they don’t fully understand.Integration Issues – Difficulty for traditional businesses
Large organizations with existing IT systems find it challenging to integrate blockchain. Shifting from centralized databases to decentralized ledgers requires costly infrastructure changes, employee training, and sometimes even a complete redesign of business processes. Small businesses may lack the resources, while big enterprises may be cautious about experimenting with such a disruptive technology.
The Future of Blockchain in 2025 and Beyond
As of 2025, blockchain is no longer a buzzword — it’s becoming part of mainstream systems. Let’s look at emerging trends:
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Countries like China, India, and the U.S. are experimenting with digital currencies powered by blockchain.
Green Blockchain: Eco-friendly consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake are reducing energy usage.
AI + Blockchain: Combining artificial intelligence and blockchain for smarter, more secure decision-making.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance): Banking without banks, giving financial access to the unbanked.
Metaverse & NFTs: Virtual worlds and digital ownership powered by blockchain.
Blockchain in Governance: Transparent public spending and corruption-free systems.
The possibilities are endless — and we’ve only scratched the surface.
Real-Life Examples of Blockchain in Action
Walmart: Uses blockchain to track food supply chains, ensuring freshness and safety.
IBM Food Trust: Works with farmers, suppliers, and retailers to improve transparency.
Ethereum: A blockchain that powers smart contracts and decentralized apps.
VeChain: Helps luxury brands fight counterfeiting with product authentication.
Estonia’s Government: Uses blockchain for secure citizen data and e-governance.
Conclusion
Blockchain (Block Technology) isn’t just a buzzword tied to Bitcoin. It’s a trust machine — enabling secure, transparent, and efficient transactions across industries.
It empowers financial systems without banks.
It strengthens supply chains with transparency.
It protects identities and intellectual property.
It builds trust where it’s been missing.
Yes, challenges like energy use and regulation exist. But as the technology evolves, blockchain is shaping up to be as fundamental to our future as the internet was to our past.
Over to You!
Do you think blockchain will replace traditional banking and governance systems in the future?![]() Drop your thoughts in the comments.
Drop your thoughts in the comments.![]() Share this post with your tech-loving friends.
Share this post with your tech-loving friends.![]() Follow us for more future tech insights.
Follow us for more future tech insights.


Its like you read my mind You appear to know so much about this like you wrote the book in it or something I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a little bit but other than that this is fantastic blog A great read Ill certainly be back
[…] you work in tech — whether you’re a developer, designer, data wizard, cloud engineer, or the unofficial office “tech guy” — you’ve […]
Easy peasy wowphlogin. Finally, a login that works without any headaches. Get in the game and start winning! wowphlogin
Really great read — I appreciate how clearly you explained the importance of local online presence for businesses today. It's a topic many companies overlook, i find it very interesting and very important topic. can i ask you a question? also we are recently checking out this newbies in the webdesign industry., you can take a look . waiting to ask my question if allowed. Thank you
Spinning the reels on 777win66 tonight. Fingers crossed for that lucky 7! Anyone else playing there? I am feeling lucky, check it out 777win66.